
- Android编程获取并设置Activity亮度的方法
- Android开发之毛玻璃效果实例代码
- Android播放视频的三种方式
- Android实现通知栏透明的方法
- Android判断当前应用程序处于前台还是后台的两种方法
- [Java4Android]22_面向对象应用(一)
- 基于Android Service 生命周期的详细介绍
- Android编程实现横竖屏切换时不销毁当前activity和锁定屏幕的方法
- 将替代ListView的RecyclerView 的使用详解(一)
- Android中asset文件夹与raw文件夹的区别深入解析
- 浅析Android 模拟键盘鼠标事件
- Android监听来电和去电的实现方法
- 在不同Activity之间传递数据的四种常用方法
- Android中监听判断网络连接状态的方法
- Android实现定时器的3种方法
- Android App中读取XML与JSON格式数据的基本方法示例
- android编程实现sd卡读取数据库的方法
- Android开发学习路线图
- Android 添加TextView删除线(代码简单)
- Android Bitmap详细介绍
- Android 3D旋转动画效果实现分解
- 探讨:你真的会用Android的Dialog吗?
- Android中的广播和广播接收器代码实例
- 在Android中访问WebService接口的方法
- Android应用开发中数据的保存方式总结
- Android手机开发 使用线性布局和相对布局实现Button垂直水平居中
- android读取Assets图片资源保存到SD卡实例
- Android中刷新界面的二种方法
- Android技巧一之启动屏+新功能左右导航逻辑
- 分享实现Android图片选择的两种方式
实例讲解Android中SQLiteDatabase使用方法
SQLite数据库是android系统内嵌的数据库,小巧强大,能够满足大多数SQL语句的处理工作,而SQLite数据库仅仅是个文件而已。虽然SQLite的有点很多,但并不是如同PC端的mysql般强大,而且android系统中不允许通过JDBC操作远程数据库,所以只能通过webservice等手段于php、servlet交互获取数据。
SQLiteDatabase类,代表了一个数据库对象,通过SQLiteDatabase来操作管理数据库。
一些基本的用法:
static SQLiteDatabase openDatabase(String path,SQLiteDatabase.CUrsorFactory factory,int flag);
static SQLiteDatabase openOrCreateDatabase(File file,SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory);
static SQLiteDatabase openOrCreateDatabase(String path,SQLiteDatabse.CursorFactory factory);
通过这些静态方法可以很方便的打开和新建一个数据库。
1、execSQL(String sql,Object[] bindArgs)
2、execSQL(String sql)
3、rawQuery(String sql,String[] selectionArgs);
4、beginTransaction()
5、endTransaction()
这些函数可以完成SQL功能,对于查询出来的结果是用Cursor表示的,类似于JDBC中的ResultSet类,在这些类中通过方法move(int offset)、moveToFirst()、moveToLast()、moveToNext()、moveToPosition(int position)、moveToPrivious()获取需要的结果行。
下面通过一个实例来说明一下SQLiteDatabase的基本使用:
main.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".Main" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="key" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/keys"
android:layout_width="100sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="value" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/values"
android:layout_width="100sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="100sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="submit" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
用于填充数据的mytextview.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/listkey"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="left" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/listvalue"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="300sp" />
</LinearLayout>
Main.java
package com.app.main;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.CursorAdapter;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class Main extends Activity {
EditText ed1 = null;
EditText ed2 = null;
Button btn = null;
ListView lv = null;
SQLiteDatabase db = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
ed1 = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.keys);
ed2 = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.values);
btn = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn);
lv = (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.lv);
db = SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(this.getFilesDir().toString()
+ "/my.db3", null);
btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String key = ed1.getText().toString();
String value = ed2.getText().toString();
try {
insertData(db, key, value);
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from tb_info", null);
inflateListView(cursor);
} catch (Exception e) {
String sql = "create table tb_info(_id integer primary key autoincrement,db_key varchar(20),db_value varchar(50))";
db.execSQL(sql);
insertData(db, key, value);
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from tb_info", null);
inflateListView(cursor);
}
}
});
}
// 向数据库中插入数据
private void insertData(SQLiteDatabase db, String key, String value) {
db.execSQL("insert into tb_info values (null,?,?)", new String[] { key,
value });
System.out.println("------------------");
}
// 向ListView中填充数据
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public void inflateListView(Cursor cursor) {
SimpleCursorAdapter adapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(Main.this,
R.layout.mytextview, cursor, new String[] { "db_key",
"db_value" },
new int[] { R.id.listkey, R.id.listvalue },
CursorAdapter.FLAG_REGISTER_CONTENT_OBSERVER);
lv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (db != null && db.isOpen()) {
db.close();
}
}
}
实现的效果:
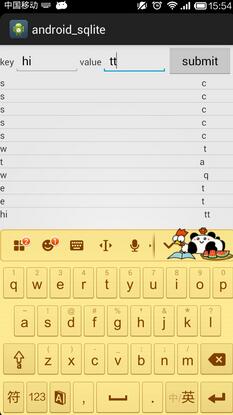
需要特别指出,在用SimpleCursorAdapter封装Cursor的时候,要求底层数据库表的主键列的列名为_id,因为SimpleCursorAdapter只能识别主键列名为_id的表。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
- 上一篇文章: 详解Android中一些SQLite的增删改查操作
- 下一篇文章: Android巧用ActionBar实现下拉式导航
- Android中AsyncTask详细介绍
- 实例详解Android解决按钮重复点击问题
- 非常简单的Android打开和保存对话框功能
- Android编程之截屏实现方法(包括scrollview
- android实现在横竖屏切换时页面信息不被重置
- Android创建文件实现对文件监听示例
- android弹出activity设置大小的方法