
- Android日期时间格式国际化的实现代码
- Android实现TextView两端对齐的方法
- Android查看电池电量的方法(基于BroadcastReceiver)
- 全面解析Android应用开发中Activity类的用法
- Android列表对话框用法实例分析
- Android编程使用Fragment界面向下跳转并一级级返回的实现方法
- Android编程实现将应用强制安装到手机内存的方法
- Android软键盘弹出时的界面控制方法
- Android ListView数据绑定显示的三种解决方法
- [Android开发从零开始].8.Activity生命周期
- Android五大布局与实际应用详解
- android 网络连接处理分析
- 解决Android SDK下载和更新失败的方法详解
- Android实现授权访问网页的方法
- Android字符串转Ascii码实例代码
- Android获取设备CPU核数、时钟频率以及内存大小的方法
- Android使用广播(BroadCast)实现强制下线的方法
- 深入分析Android ViewStub的应用详解
- Android图片缓存之Lru算法(二)
- Windows下快速搭建安卓开发环境Android studio
- 如何在XML中定义菜单
- 使用OkHttp包在Android中进行HTTP头处理的教程
- Android 数据库SQLite 写入SD卡的方法
- 全面解析Android中对EditText输入实现监听的方法
- Android实现跑马灯效果的方法
- android多行标签热点示例
- Android使用Sensor感应器获取用户移动方向(指南针原理)
- Android 底部导航控件实例代码
- Android开发 -- setTag的妙用和The key must be an application-specific resource id 异常
- Android招聘面试题解答
Android控件之Gallery用法实例分析
作者:佚名 Android开发编辑:admin 更新时间:2022-07-23
本文实例讲述了Android控件之Gallery用法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下:
Gallery组件主要用于横向显示图像列表,不过按常规做法。Gallery组件只能有限地显示指定的图像。也就是说,如果为Gallery组件指定了10张图像,那么当Gallery组件显示到第10张时,就不会再继续显示了。这虽然在大多数时候没有什么关系,但在某些情况下,我们希望图像显示到最后一张时再重第1张开始显示,也就是循环显示。要实现这种风格的Gallery组件,就需要对Gallery的Adapter对象进行一番改进。
以下通过Gallery模拟循环显示图像,在单击某一个Gallery组件中的图像时在下方显示一个放大的图像(使用ImageSwitcher组件)。
目录结构
main.xml布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <!-- android:unselectedAlpha: 设置未选中的条目的透明度(Alpha)。该值必须是float类型,比如:“1.2”。 --> <Gallery android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:spacing="10dip" android:unselectedAlpha="1.2" android:id="@+id/gallery" android:layout_marginTop="30dp"/> <ImageSwitcher android:id="@+id/imageSwitcher" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="30dp" /> </LinearLayout>
GalleryActivity类:
package com.ljq.ga;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.AnimationUtils;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.Gallery;
import android.widget.ImageSwitcher;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener;
import android.widget.LinearLayout.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.ViewSwitcher.ViewFactory;
public class GalleryActivity extends Activity implements ViewFactory {
private Gallery gallery = null;
private ImageSwitcher imageSwitcher=null;
int[] imageIDs={
R.drawable.p1,R.drawable.p2,R.drawable.p3,
R.drawable.p4,R.drawable.p5,R.drawable.p6,
R.drawable.p7,R.drawable.p8 };
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
imageSwitcher=(ImageSwitcher)findViewById(R.id.imageSwitcher);
// 设置ImageSwitcher组件的工厂对象
imageSwitcher.setFactory(this);
// 设置ImageSwitcher组件显示图像的动画效果
imageSwitcher.setInAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.fade_in));
imageSwitcher.setOutAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this,
android.R.anim.fade_out));
gallery = (Gallery) findViewById(R.id.gallery);
ImageViewAdapter adapter=new ImageViewAdapter(GalleryActivity.this, imageIDs);
gallery.setAdapter(adapter);
gallery.setOnItemSelectedListener(new OnItemSelectedListener(){
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
//选中Gallery中某个图像时,在ImageSwitcher组件中放大显示该图像
imageSwitcher.setImageResource(imageIDs[position%imageIDs.length]);
}
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> arg0) {
}
});
gallery.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener(){
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
Log.i("ljq", "parent="+parent.getClass().getName()); //Gallery
Log.i("ljq", "view="+view.getClass().getName()); //ImageView
Log.i("ljq", "position=" + position); //1
Log.i("ljq", "id=" + id);//1
Gallery gl=(Gallery)parent;
ImageView iv=(ImageView)view;
}
});
}
// ImageSwitcher组件需要这个方法来创建一个View对象(一般为ImageView对象)
// 来显示图像
public View makeView() {
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(this);
imageView.setBackgroundColor(0xFF000000);
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_CENTER);
imageView.setLayoutParams(new ImageSwitcher.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT));
return imageView;
}
}
ImageViewAdapter自定义适配器:
package com.ljq.ga;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class ImageViewAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private int[] imageIDs=null;
private Context context=null;
public ImageViewAdapter(Context context, int[] imageIDs) {
this.context=context;
this.imageIDs=imageIDs;
}
//用于返回图像总数,要注意的是,这个总数不能大于图像的实际数(可以小于图像的实际数),否则会抛出越界异常。
public int getCount() {
//优化一
//return imageIDs.length;
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public Object getItem(int position) {
return imageIDs[position];
}
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
//ScaleType的用法
//CENTER/center 按图片的原来size居中显示,当图片长/宽超过View的长/宽,则截取图片的居中部分显示
//CENTER_CROP/centerCrop 按比例扩大图片的size居中显示,使得图片长 (宽)等于或大于View的长(宽)
//CENTER_INSIDE/centerInside 将图片的内容完整居中显示,通过按比例缩小 或原来的size使得图片长/宽等于或小于View的长/宽
//FIT_CENTER/fitCenter 把图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,居中显示
//FIT_END/fitEnd 把 图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,显示在View的下部分位置
//FIT_START/fitStart 把 图片按比例扩大/缩小到View的宽度,显示在View的上部分位置
//FIT_XY/fitXY 把图片 不按比例 扩大/缩小到View的大小显示
//MATRIX/matrix 用矩阵来绘制
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ImageView iv = new ImageView(context);
//优化二,通过取余来循环取得imageIDs数组中的图像资源ID,取余可以大大较少资源的浪费
iv.setImageResource(imageIDs[position%imageIDs.length]);
iv.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE);
iv.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(77,77));//把图片缩小原来的60%
return iv;
}
}
运行结果
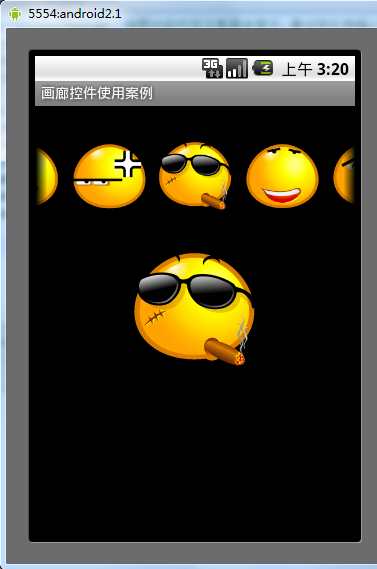
希望本文所述对大家的Android程序设计有所帮助。
- 上一篇文章: Android模拟美团客户端进度提示框
- 下一篇文章: Android控件之TabHost用法实例分析
- 利用源码编译Android系统的APK和可执行命令
- 图解Windows环境下Android Studio安装和使用
- Android实现从网络获取图片显示并保存到SD卡
- Android 设置应用全屏的两种解决方法
- Android屏蔽EditText软键盘的方法
- 安装时加入外部数据库示例(android外部数据
- Android编程实现QQ表情的发送和接收完整实例